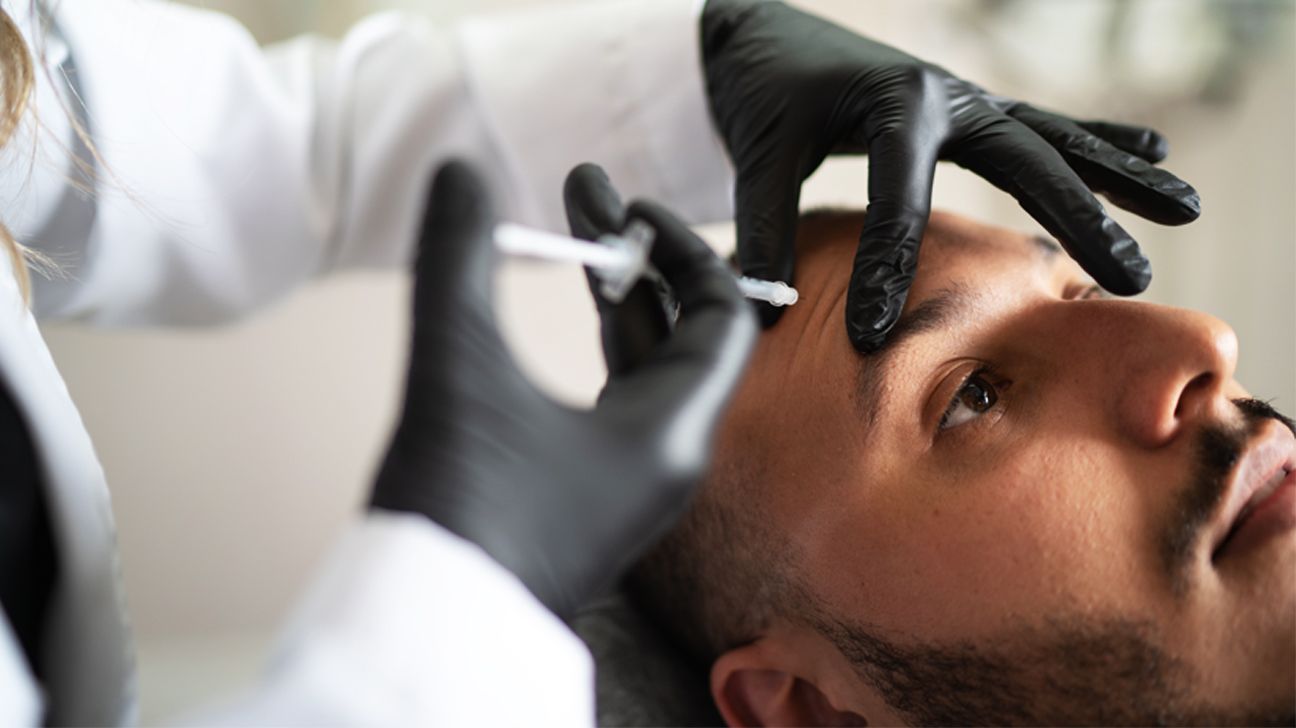
- A new report from the CDC found that 19 women in nine states became ill after Botox injections.
- Botulism can lead to symptoms such as muscle paralysis, blurred or double vision, slurred speech, difficulty breathing, and in some cases, death.
- To ensure safety, it’s important to go to a board-certified dermatologist and ask questions about the product being used before the procedure.
The CDC released a health advisory on April 15 regarding an ongoing investigation of adverse reactions associated with counterfeit or mishandled Botox injections.
As of April 12, 19 people from 9 states claimed to have experienced harmful reactions after receiving Botox injections from unlicensed or inadequately trained individuals in non-healthcare environments, including homes and spas.
Out of the 19 patients, 9 were hospitalized and 4 were given botulism antitoxin due to the possibility that the botulinum toxin could have spread throughout the body.
These states included Colorado, Florida, Illinois, Kentucky, Nebraska, New Jersey, New York, Tennessee, and Washington.
For those who are seeking Botox injections, the CDC advised, “ask your provider and setting (such as clinic or spa) if they are licensed and trained to give the injection” and “ask if the product is approved by FDA and obtained from a reliable source.”
What to know about Botox
Botox, is an injectable neurotoxin derived from botulinum toxin type A. This substance is naturally produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum.
“Botox blocks the nervous system from releasing acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter, to targeted muscles and cause a temporary muscle paralysis,” said Michele Green, MD, a cosmetic dermatologist at Northwell Lenox Hill Hospital.
“When injected into areas of the face such as the forehead, between the eyebrows, and the corners of the eyes, Botox essentially ‘freezes’ the muscles that create dynamic fine lines and wrinkles in the area.”
Tien Nguyen, MD, board-certified dermatologist at MemorialCare Orange Coast Medical Center in Fountain Valley, CA, told Healthline Botox was developed in the 90s by the pharmaceutical company Allergan for medical purposes as well as cosmetic purposes.
“At controlled, low dosage, injections in small and controlled amount directly in the muscle will create muscle weakness, achieving the target you want,” Nguyen said.
What does botulism do to the body?
Botulism develops from the botulinum toxin attacking the body’s nervous system. It can cause muscle paralysis, blurred or double vision, slurred speech, difficulty breathing, and in severe cases, death.
“The botulism toxin arises from Clostridium botulinum, the same bacterium used to crease Botox,” Green said.
“This bacterium can be found in many places and are commonly consumed by individuals without any resulting sickness.”
However, in certain conditions, spores created by the bacterium will grow and release the botulism toxin.
Foods that are improperly preserved, fermented, or home-canned are common places where spores thrive and release botulism toxin, Green added.
How do you know Botox is safe?
There are several things to keep in mind before trying Botox.
“When considering a Botox service, it is incredibly important to ensure that the provider performing the procedure is a board-certified dermatologist or plastic surgeon using regulated products,” said Green. “While medical spas may be more cost-effective, only a board certified healthcare provider can provide you with the safest and most effective Botox treatment.”
It’s also important to note there are other types of Botox made globally: Xeomin from Germany, Dysport from Europe and several more companies are making similar toxin for commercial usage, Nguyen explained.
What to do if you receive fake Botox
Experts agreed it is important to see a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
“If you are concerned that you may have received counterfeit Botox and are experiencing any adverse side effects, it is important to get immediate medical attention. You should either see a doctor or go to an emergency room,” Green stated.
Patients should ask questions about what is being injected before the procedure.
“There are millions of healthcare providers injecting Botox-like products,” said Nguyen.
“It may not be just the only Botox coming from Allergan anymore. The consumer (patients) should be aware of what is being used for their injection for safety.”
Takeaway
A new health advisory from the CDC reported 19 women in nine states becoming sick after Botox injections.
Botulism can cause muscle paralysis, blurred or double vision, slurred speech, difficulty breathing, and in some cases, death.
It’s crucial to go to a board-certified dermatologist and ask questions about the product beforehand.
Counterfeit Botox Caused Botulism Reactions In 9 U.S. States, CDC Says
Source: Pinoy Lang Sakalam



0 (mga) komento:
Mag-post ng isang Komento